Direct, stereoselective thioglycosylation enabled by an organophotoredox radical strategy†
Abstract
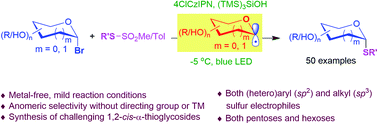
While strategies involving a 2e− transfer pathway have dictated glycosylation development, the direct glycosylation of readily accessible glycosyl donors as radical precursors is particularly appealing because of high radical anomeric selectivity and atom- and step-economy. However, the development of the radical process has been challenging owing to notorious competing reduction, elimination and/or SN side reactions of commonly used, labile glycosyl donors. Here we introduce an organophotocatalytic strategy through which glycosyl bromides can be efficiently converted into corresponding anomeric radicals by photoredox mediated HAT catalysis without a transition metal or a directing group and achieve highly anomeric selectivity. The power of this platform has been demonstrated by the mild reaction conditions enabling the synthesis of challenging α-1,2-cis-thioglycosides, the tolerance of various functional groups and the broad substrate scope for both common pentoses and hexoses. Furthermore, this general approach is compatible with both sp2 and sp3 sulfur electrophiles and late-stage glycodiversification for a total of 50 substrates probed.
Description
Indexed in scopushttps://www.scopus.com/authid/detail.uri?authorId=57202719978 |
Article metrics10.31763/DSJ.v5i1.1674 Abstract views : | PDF views : |
Cite |
Full Text Download Download
|
Conflict of interest
“Authors state no conflict of interest”
Funding Information
This research received no external funding or grants
Peer review:
Peer review under responsibility of Defence Science Journal
Ethics approval:
Not applicable.
Consent for publication:
Not applicable.
Acknowledgements:
None.